Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal
Return the root node of a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
(Recall that a binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of node.left has a value < node.val, and any descendant of node.right has a value > node.val. Also recall that a preorder traversal displays the value of the node first, then traverses node.left, then traverses node.right.)
It's guaranteed that for the given test cases there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements.
Example 1:
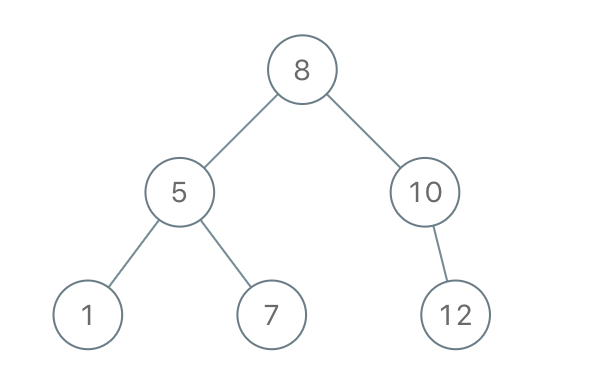
Input: [8,5,1,7,10,12] Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 100
1 <= preorder[i] <= 10^8
The values of preorder are distinct
Solution in Java:
public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) {
if(preorder == null || preorder.length == 0){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<TreeNode>();
stk.push(root);
for(int i = 1; i<preorder.length; i++){
TreeNode cur = new TreeNode(preorder[i]);
TreeNode top = stk.peek();
while(!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek().val<preorder[i]){
top = stk.pop();
}
if(top.val < preorder[i]){
top.right = cur;
}else{
top.left = cur;
}
stk.push(cur);
}
return root;
}
}

Comments
Post a Comment