Remove Linked List Elements
Topic : Recursion
Given the head of a linked list and an integer val, remove all the nodes of the linked list that has Node.val == val, and return the new head.
Example 1:
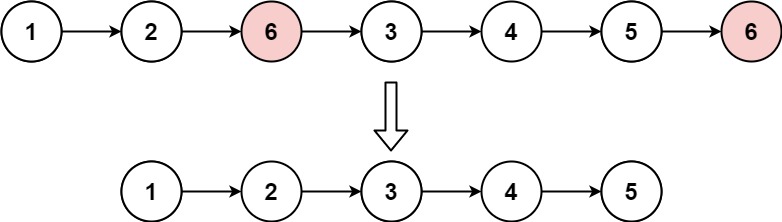
Input: head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [], val = 1 Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 500 <= val <= 50
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
if(head -> val != val){
head -> next = removeElements(head -> next, val);
return head;
}
else{
ListNode* newHead = head -> next;
return removeElements(newHead, val);
}
}
};Perfect Solution :
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { if(head == nullptr) return head; //for starting values while(head!=nullptr && head->val == val){ //for beggining head=head->next; } ListNode* temp = head; while(temp != nullptr && temp->next != nullptr){ if(temp->next->val == val){ temp->next = temp->next->next; }else{ temp = temp->next; } } return head; } };
Comments
Post a Comment