Uncrossed Lines
We write the integers of A and B (in the order they are given) on two separate horizontal lines.
Now, we may draw connecting lines: a straight line connecting two numbers A[i] and B[j] such that:
A[i] == B[j];
The line we draw does not intersect any other connecting (non-horizontal) line.
Note that a connecting lines cannot intersect even at the endpoints: each number can only belong to one connecting line.
Return the maximum number of connecting lines we can draw in this way.
Now, we may draw connecting lines: a straight line connecting two numbers A[i] and B[j] such that:
A[i] == B[j];
The line we draw does not intersect any other connecting (non-horizontal) line.
Note that a connecting lines cannot intersect even at the endpoints: each number can only belong to one connecting line.
Return the maximum number of connecting lines we can draw in this way.
Example 1:
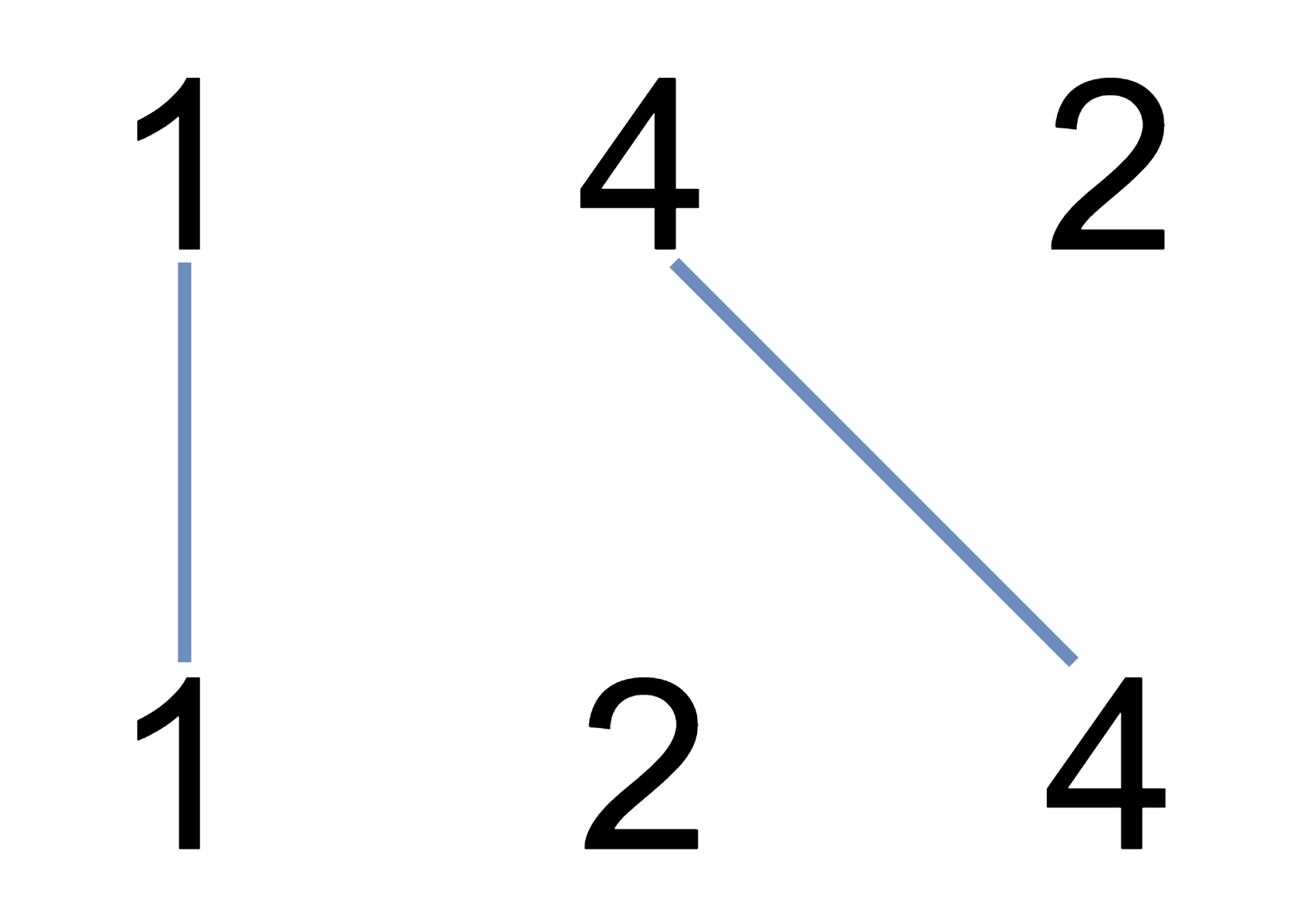
Input: A = [1,4,2], B = [1,2,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: We can draw 2 uncrossed lines as in the diagram.
We cannot draw 3 uncrossed lines, because the line from A[1]=4 to B[2]=4 will intersect the line from A[2]=2 to B[1]=2.
Example 2:
Input: A = [2,5,1,2,5], B = [10,5,2,1,5,2]
Output: 3
Example 3:
Input: A = [1,3,7,1,7,5], B = [1,9,2,5,1]
Output: 2
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 500
1 <= B.length <= 500
1 <= A[i], B[i] <= 2000
Example 2:
Input: A = [2,5,1,2,5], B = [10,5,2,1,5,2] Output: 3
Example 3:
Input: A = [1,3,7,1,7,5], B = [1,9,2,5,1] Output: 2
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 500
1 <= B.length <= 500
1 <= A[i], B[i] <= 2000
Solution in Python :
class Solution(object):
def maxUncrossedLines(self, A, B):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:type B: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
memo={}
la,lb=len(A),len(B)
def helper(i,j):
if i>=la or j>=lb:
return 0
if (i,j) in memo:
return memo[i,j]
if A[i]==B[j]:
ans=1+helper(i+1,j+1)
else:
ans=max(helper(i+1,j),helper(i,j+1))
memo[i,j]=ans
return ans
return helper(0,0)
Comments
Post a Comment